Interaction between phylogenetic uncertainty and intraspecific variability - Phylogenetic logistic Regression
Source:R/tree_intra_phyglm.R
tree_intra_phyglm.RdPerforms Phylogenetic logistic regression evaluating intraspecific variability in response and/or predictor variables and uncertainty in trees topology.
tree_intra_phyglm( formula, data, phy, Vx = NULL, x.transf = NULL, n.intra = 10, n.tree = 2, distrib = "normal", track = TRUE, btol = 50, ... )
Arguments
| formula | The model formula: |
|---|---|
| data | Data frame containing species traits and species names as row names. |
| phy | A phylogeny (class 'phylo', see ? |
| Vx | Name of the column containing the standard deviation or the standard error of the predictor
variable. When information is not available for one taxon, the value can be 0 or |
| x.transf | Transformation for the predictor variable (e.g. |
| n.intra | Number of times to repeat the analysis generating a random value for response and/or predictor variables.
If NULL, |
| n.tree | Number of times to repeat the analysis with n different trees picked
randomly in the multiPhylo file.
If NULL, |
| distrib | A character string indicating which distribution to use to generate a random value for the response
and/or predictor variables. Default is normal distribution: "normal" (function |
| track | Print a report tracking function progress (default = TRUE) |
| btol | Bound on searching space. For details see |
| ... | Further arguments to be passed to |
Value
The function tree_intra_phylm returns a list with the following
components:
formula: The formula
data: Original full dataset
sensi.estimates: Coefficients, aic and the optimised value of the phylogenetic
parameter (e.g. lambda) for each regression using a value in the interval of variation and
a different phylogenetic tree.
N.obs: Size of the dataset after matching it with tree tips and removing NA's.
stats: Main statistics for model parameters.CI_low and CI_high are the lower
and upper limits of the 95
all.stats: Complete statistics for model parameters.
Fields coded using all describe statistics due to both intraspecific variation and phylogenetic uncertainty.
Fields coded using intra describe statistics due to intraspecific variation only.
Fields coded using tree describe statistics due to phylogenetic uncertainty only.
sd is the standard deviation. CI_low and CI_high are the lower and upper limits
of the 95
sp.pb: Species that caused problems with data transformation (see details above).
Details
This function fits a phylogenetic logistic regression model using phyloglm to n trees (n.tree),
randomly picked in a multiPhylo file. The regression is also repeated n.intra times.
At each iteration the function generates a random value for each row in the dataset using the standard deviation
or errors supplied and assuming a normal or uniform distribution. To calculate means and se for your raw data,
you can use the summarySE function from the package Rmisc.
#' All phylogenetic models from phyloglm can be used, i.e. BM,
OUfixedRoot, OUrandomRoot, lambda, kappa,
delta, EB and trend. See ?phyloglm for details.
Currently, this function can only implement simple logistic models (i.e. \(trait~ predictor\)). In the future we will implement more complex models.
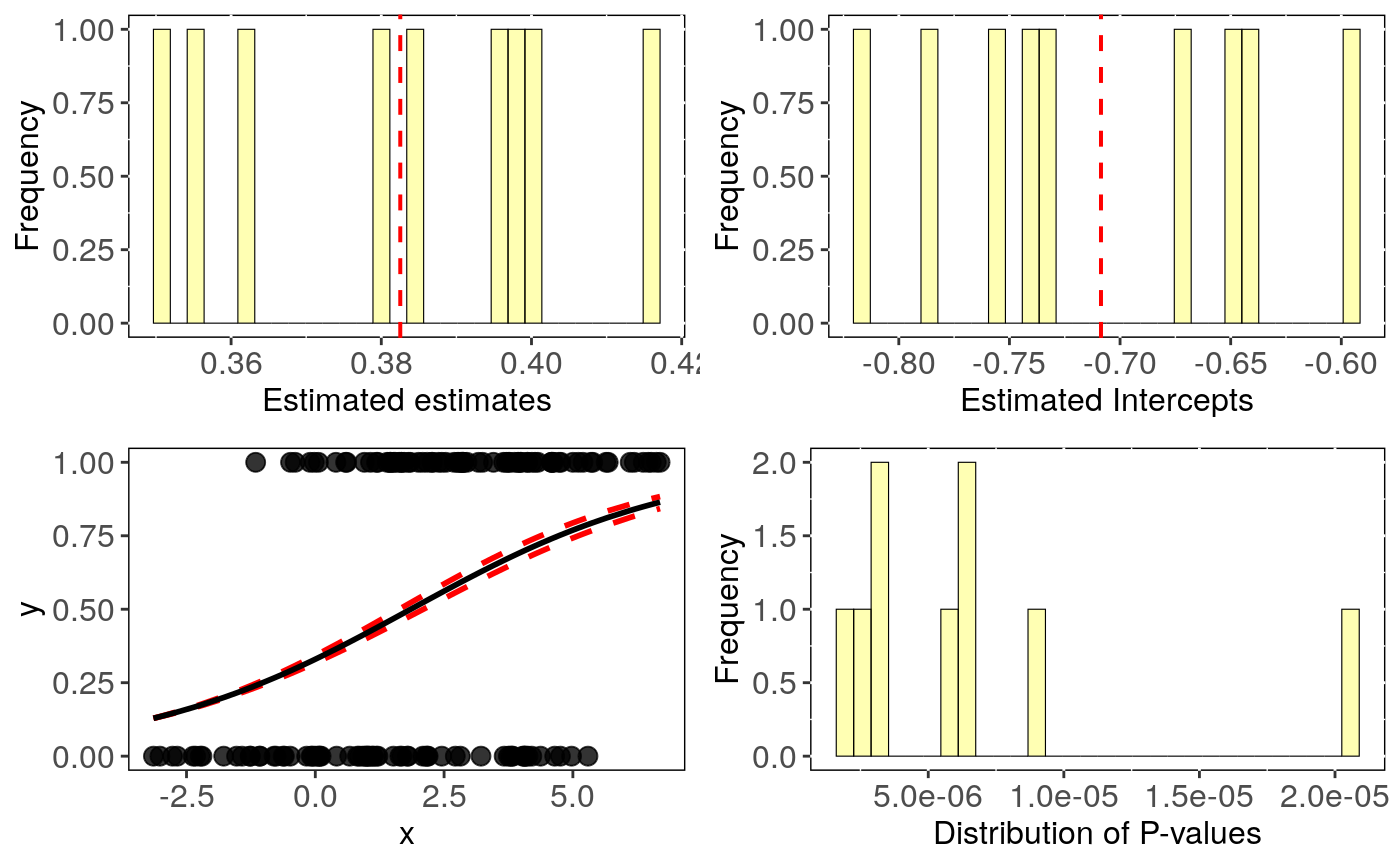
Output can be visualised using sensi_plot.
Warning
When Vy or Vx exceed Y or X, respectively, negative (or null) values can be generated, this might cause problems
for data transformation (e.g. log-transformation). In these cases, the function will skip the simulation. This problem can
be solved by increasing times, changing the transformation type and/or checking the target species in output$sp.pb.
References
Paterno, G. B., Penone, C. Werner, G. D. A. sensiPhy: An r-package for sensitivity analysis in phylogenetic comparative methods. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 2018, 9(6):1461-1467
Martinez, P. a., Zurano, J.P., Amado, T.F., Penone, C., Betancur-R, R., Bidau, C.J. & Jacobina, U.P. (2015). Chromosomal diversity in tropical reef fishes is related to body size and depth range. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 93, 1-4
Ho, L. S. T. and Ane, C. 2014. "A linear-time algorithm for Gaussian and non-Gaussian trait evolution models". Systematic Biology 63(3):397-408.
See also
Examples
# Simulate data set.seed(6987) mphy = ape::rmtree(150, N = 30) x = phylolm::rTrait(n=1,phy=mphy[[1]]) x_sd = rnorm(150,mean = 0.8,sd=0.2) X = cbind(rep(1,150),x) y = rbinTrait(n=1,phy=mphy[[1]], beta=c(-1,0.5), alpha=.7 ,X=X) dat = data.frame(y, x, x_sd) intra.tree <- tree_intra_phyglm(y ~ x, data = dat, phy = mphy, n.intra = 3, n.tree = 3, Vx = "x_sd")#> Warning: distrib = normal: make sure that standard deviation is provided for Vx and/or Vy#>#> | | | 0%#> Warning: the estimate of 'alpha' (10.4601876142051) reached the upper bound (10.4649228412699). #> This may simply reflect a flat likelihood at large alpha values, #> meaning that the phylogenetic correlation is estimated to be negligible.#> Warning: the estimate of 'alpha' (10.4560158891315) reached the upper bound (10.4649228412699). #> This may simply reflect a flat likelihood at large alpha values, #> meaning that the phylogenetic correlation is estimated to be negligible.#> | |======================= | 33% | |=============================================== | 67% | |======================================================================| 100%#> mean.all min.tree sd_tree min.intra max.tree CI_low_tree #> intercept -0.709 -0.731 0.039 -0.746 -0.663 -0.811 #> se.intercept 0.252 0.246 0.005 0.246 0.254 0.239 #> pval.intercept 0.006 0.005 0.002 0.004 0.008 0.002 #> estimate 0.383 0.377 0.008 0.372 0.391 0.356 #> se.estimate 0.084 0.083 0.001 0.083 0.084 0.081 #> pval.estimate 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 #> CI_low_intra mean.tree CI_high_tree #> intercept -0.811 -0.709 -0.607 #> se.intercept 0.239 0.252 0.265 #> pval.intercept 0.002 0.006 0.010 #> estimate 0.356 0.383 0.410 #> se.estimate 0.081 0.084 0.086 #> pval.estimate 0.000 0.000 0.000# Visual diagnostics for phylogenetic uncertainty: sensi_plot(intra.tree, uncer.type = "all") #or uncer.type = "tree", uncer.type = "intra"